| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 |
- Kotlin
- sockettimeout
- 데이터 이해
- MySQL
- watchman error
- 자료구조
- 쿼리문
- h2 error
- kotlin recyclerview checkbox error
- GitHub
- expo-cli error
- kotlin checkbox error
- watchmanresponse
- retrofit
- 선택정렬
- ADsP
- Today
- Total
Stand up lee
병합 정렬(merge sort) 본문
병합 정렬(merge sort)란
분할정복 알고리즘 중 하나로 재귀용법을 활용한 정렬 알고리즘이다.
1. 리스트를 절반으로 잘라 비슷한 크기의 두 부분 리스트로 나눈다
2. 각 부분 리스트를 재귀적으로 합병 정렬을 이용해 정렬한다
3. 두 부분 리스트를 다시 하나의 정렬된 리스트로 합병한다
예를 들어 data_list = [1, 9, 3, 2]
-
- 먼저 [1, 9], [3, 2] 로 나누고
- [1] [9] 로 나눈다
- 정렬해서 합친다. [1, 9]
- 다음 [3, 2] 도 [3] [2] 로 나눈다
- 정렬해서 합친다 [2, 3]
- 이제 [1, 9] 와 [2, 3]을 합친다.
- 1 < 2 이니 [1]
- 9 > 2 이니 [1, 2]
- 9 > 3 이니 [1, 2, 3]
- 9 밖에 없으니, [1, 2, 3, 9]
🎵 알고리즘 구현
1. split 함수 : 만약 리스트 갯수가 1개이면 해당 값 리턴
그렇지 않으면 리스트를 앞 뒤 두개로 나누기 left / right
-> merge(left, right)
2. merge 함수 : left와 right의 리스트 데이터를 정렬해서 sortedlist로 return
left 부터 하나씩 right과 비교
left > right 이면 left를 sortedlist에 넣고 다음 left와 right 비교
=> 재귀용법 활용하기
- left_index, right_index = 0
- while left_index < len(left) or right_index < len(right):
- 만약 left_index 나 right_index 가 이미 left 또는 right 리스트를 다 순회했다면, 그 반대쪽 데이터를 그대로 넣고, 해당 인덱스 1 증가
- if left[left_index] < right[right_index]:
- sorted.append(left[left_index])
- left_index += 1
- else:
- sorted.append(right[right_index])
- right_index += 1
import random
def mergesort(data):
if len(data) <= 1:
return data
else:
med = int(len(data)/ 2)
left = mergesort(data[:med])
right = mergesort(data[med:])
return merge(left,right)
def merge(left, right):
sortedlist = []
left_idx, right_idx = 0, 0
while left_idx < len(left) and right_idx < len(right):
if left[left_idx] < right[right_idx]:
sortedlist.append(left[left_idx])
left_idx += 1
elif left[left_idx] > right[right_idx]:
sortedlist.append(right[right_idx])
right_idx += 1
#merge하다가 한쪽만 데이터가 남았을 경우,
if left_idx >= len(left):
sortedlist = sortedlist + right[right_idx:]
if right_idx >= len(right):
sortedlist = sortedlist + left[left_idx:]
print(sortedlist)
return sortedlist
testlist = random.sample(range(100), 10)
print(testlist)
mergesort(testlist)
random으로 나온 list Input: [74, 76, 0, 86, 52, 51, 98, 82, 57, 10]
[74, 76, 0, 86, 52 // 51, 98, 82, 57, 10]
[74, 76 // 0, 86, 52 ] // [51, 98 // 82, 57, 10]
[74 // 76] // [0 // 86, 52 ] // [51 // 98] // [82 // 57, 10]
가장 첫번째 left / right부터 정렬 시작
[74, 76]
[52, 86]
[0, 52, 86]
[0, 52, 74, 76, 86]
[51, 98]
[10, 57]
[10, 57, 82]
[10, 51, 57, 82, 98]
[0, 10, 51, 52, 57, 74, 76, 82, 86, 98]
Output : [0, 10, 51, 52, 57, 74, 76, 82, 86, 98]
🎵 알고리즘 분석
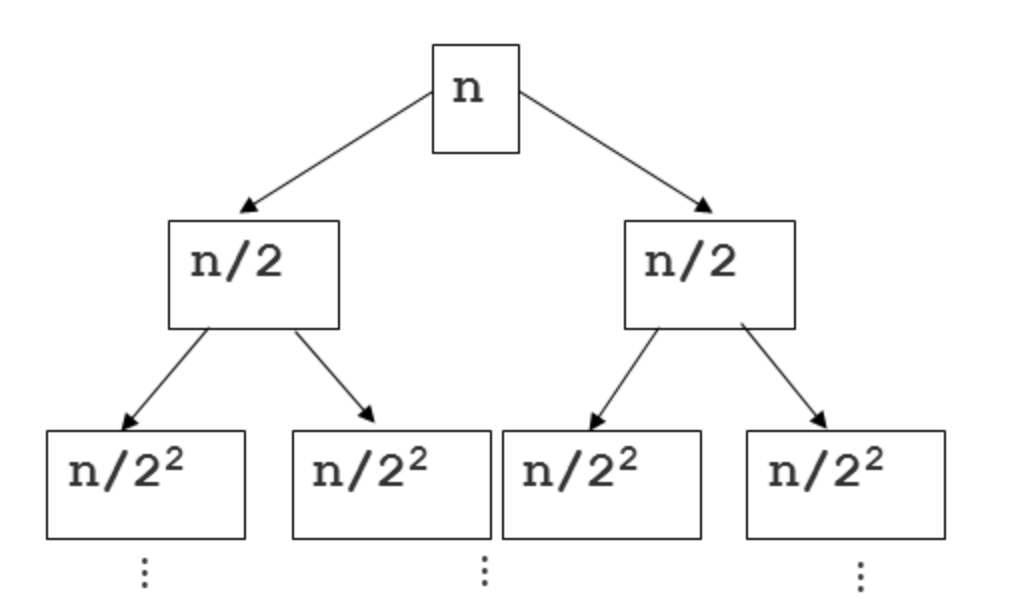
각 단계 별로 n, 2/n 2번, 4/n 4번... 만큼의 정렬 * depth 마다 걸림 --> N * logN
'자료구조&알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 삽입 정렬 (insertion sort) (0) | 2021.09.28 |
|---|---|
| 선택 정렬 (0) | 2021.06.04 |
